There are several reasons why people use Grid-Tied solar power, and you are about to learn all about it. From what a Grid-Tied solar power system is, and how it forms part of your practical life, all the way to the pros and cons. So, let’s start with what this system comprises of.
What Is Grid-Tied Solar Power?
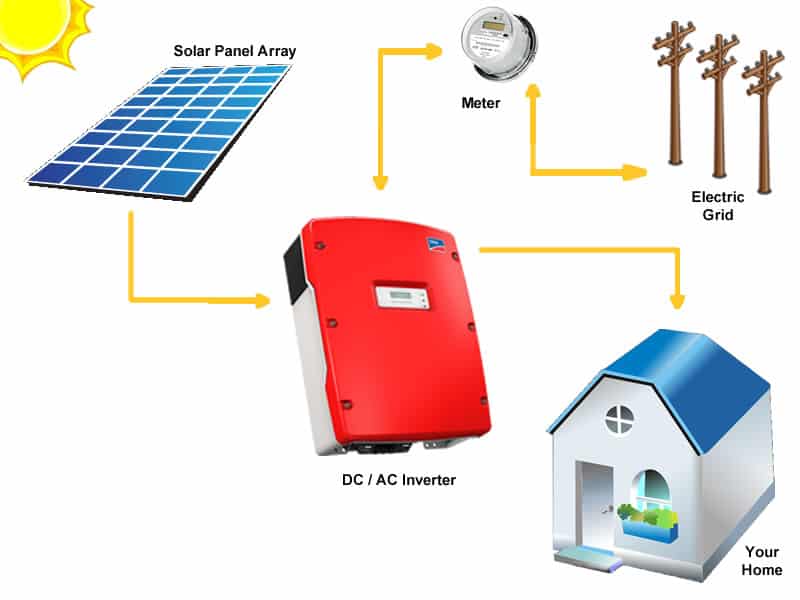
A Grid-Tied solar power system is mainly used by home or business owners as a supplementary source of energy. Battery banks are excluded from this system, so it works mostly on demand during the day.
As the demand load requires, the solar array will supply the available power that is producing at that point in time to supplement as much as what is available to the load and take the remainder from the grid to ensure the load is fulfilled.
But if it happens that your solar system is powerful enough, you can still remain tied to the grid. Then, the grid can serve as backup on those heavily packed days when the sun just doesn’t want to shine.
No, it’s not a very complicated system. And as you can see, it’s a setup that offers a lot of options. In fact, the odds of you getting caught with the lights off become very slim. Now that you know what the Grid-Ttied solar system is all about, let’s look at the pros and cons.
The Pros of a Grid-Tied Solar System
- You have two independent sources of power
There’s not much to add to this point, because it really speaks for itself. But also, take a moment to appreciate that it will take more than bad luck and mismanagement to leave you powerless.
- Make a big dent in your electricity bill
If your electricity use is mainly used in the daylight times, you are in luck. These systems are the most sensible and offer the best ROI due to the exclusion of the battery bank costs which are known to be the Achilles of Solar Power.
- It’s an affordable option
Due to the basic nature of Grid-Tied solar systems, being simply panels, inverter, perhaps lightening protections and monitoring, they are extremely inexpensive when compared to the payback period and ROI you will yield. Often a 2-4 year ROI is easily obtained from the use of these systems when you use more electricity in the daytime.
- Easy to install
Again due to the simplicity of these systems, they are extremely easy to install, therefore installation costs are kept to a minimum. Simple to use and no need for any AC re-wiring, they can supply the total load without the risk of shutting off due to overloading as the Off-Grid / energy storage systems do.
The Cons
Just to warn you beforehand, the con list is incredibly short. But you have to search really deep if you want to find anything wrong with a Grid-Tied array, even when you compare it to the other options. However, we did manage to find two possible cons.
- The grid must be present
Grid-Tied systems are completely dependent on the grid being present. The synchronize with the grid to know how much to supply. If the grid goes down, there is no power.
- Upgrading to an Off-Grid
Because these inverters used for a Grid-Tied system only have the one application, should you want to add a storage system at a later stage, they would not be able to be used. You would be able to create a separate off-grid system to supply a portion of your load for which it can handle however if the grid was to go down, you lose the power from these Grid-Tied systems altogether.
A Special Tip for Businesses
We are ending this guide with a special tip for all the businesses that operate during the day. Most businesses operate in the day times. Due to the energy only being used in the day, these systems are a perfect solution.
The more power you use in the day, the faster your ROI. Any company that uses light to heavy machinery would undoubtedly be unable to reject the sense of investment that these Grid-Tied systems offer.
