Inverter battery backup systems are very much needed in South Africa as we face more and more load shedding.
But you may not know what home battery backup solution is right for you.
In this guide, you’ll learn everything there is to know about Inverter Battery load shedding solutions and how to size them.
Contents:
- Load Shedding Solutions
- Why choose a Battery Inverter Kit?
- How Battery Inverter Kits work?
- Inverter Battery Kit includes
- Inverter Battery Kit prices
- How to choose the right equiment
- Sizing a battery bank
- Battery mounting
- Load Shedding Kit vs Solar Power Kit
Chapter 1
Load Shedding Solutions
What are the options?
For the purpose of this article, I’ll stick to residential solutions.
UPS

A UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) is a relatively small piece of equipment that will enable you to keep simple appliances running like your modem, computer and charge your phone.
Pros
- Least Expensive
- No need for Installation
Cons
- Not expandable
- Can only run small appliances
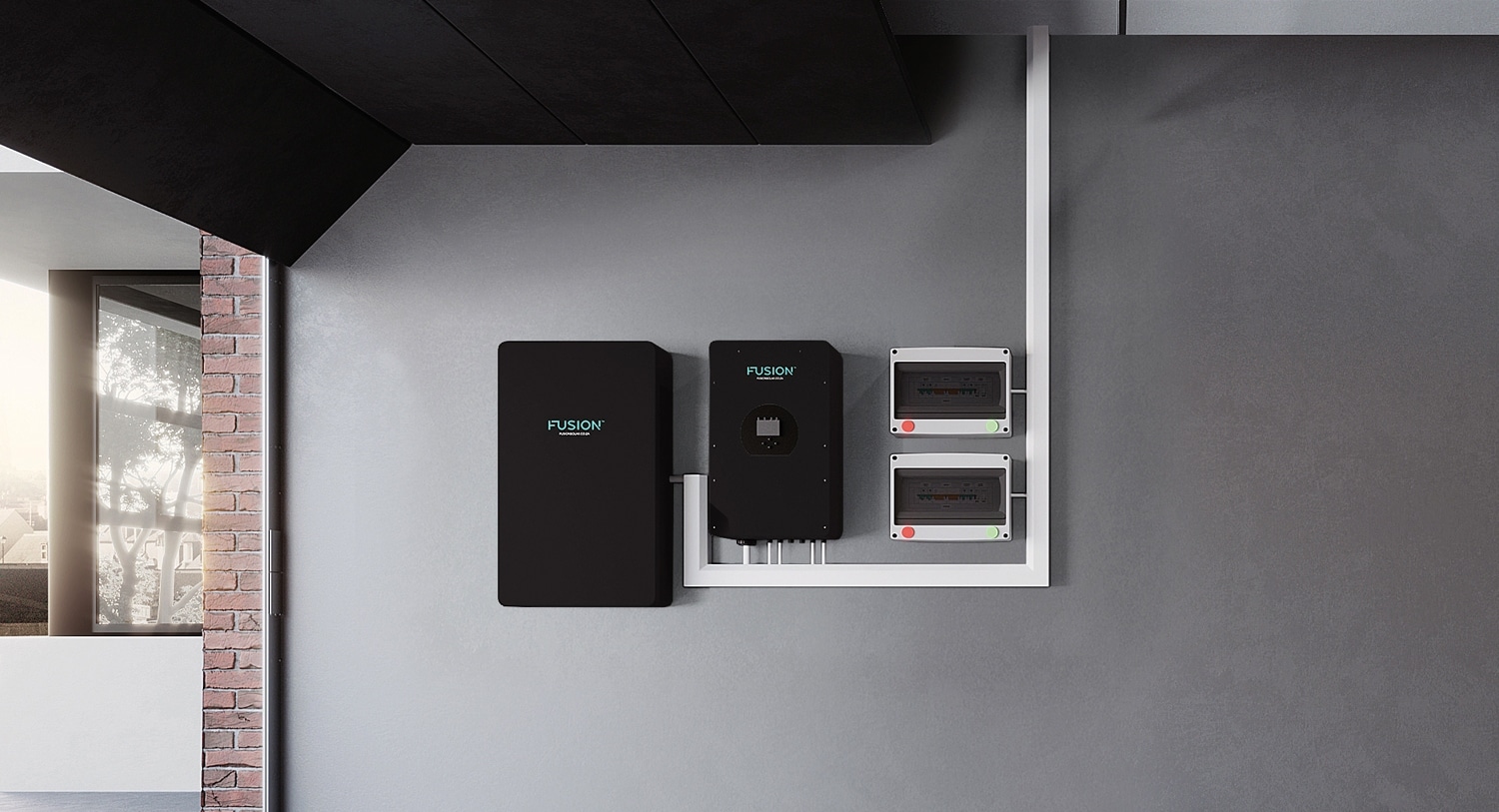
Load Shedding Unit
Load Shedding Units are usually a box with an inverter and battery inside them. They are typically larger in battery capacity than the UPS and range from 1 – 4kW.
Pros
- Portable
- No installation required
Cons
- Not expandable
- Heavy
Built-In Load Shedding Inverter Battery Kit
Built-in kits are larger than the two solutions mentioned previously and consist of an inverter, batteries and a peripheral kit.
Pros
- Run more appliances
- Built-in system
- Expandable
- Add solar later
Cons
- More expensive
Chapter 2
Why Choose a Load Shedding Inverter Battery Kit?
The breakdown
Inverter battery solutions are an excellent option for future growth and energy independence. Not to mention they are green, sustainable and renewable, making them the perfect way to protect and plan for your future.
- More affordable
- Expandable
- Can be converted into a Solar Power Kit
- Quick & easy installation
- Gives you emergency power
- Comes with everything you need for installation
- Efficient
- Safe
Chapter 3
How do Load Shedding Inverter Battery Kits work?
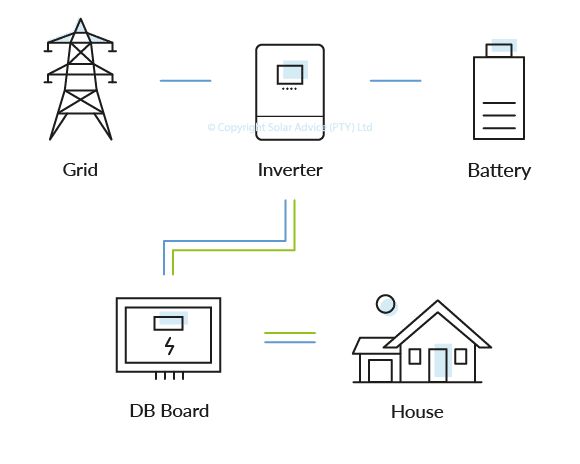
AC/DC
The inverter will pull AC power from the grid and convert it to DC power which will be stored in your battery bank. Then the inverter will convert the DC power stored in your battery into AC power and feed the converted power into your home via your DB.
An Inverter Battery Kit will only be used when there is no grid supply.
The battery will not be cycled at night like with Solar Power Kits because the power stored is for emergency backup.
It’s pointless to cycle a battery that has harvested power from the grid if you have grid supply.
Chapter 4
Load Shedding Inverter Battery Kit Includes
What’s in the box?
Let’s recap what role each piece of equipment plays and why they are necessary.
Solar Inverter

Solar panels produce and batteries store Direct Current (DC) power which is unusable by our Alternating Current (AC) appliances.
The inverter will convert DC to AC and AC to DC power to be stored and used as needed.
Read our Solar Inverter Guide
Solar Battery Bank
The battery bank is where you store harvested power to use when there is no alternative power supply. Or when there is no solar power being produced.
Read our Solar Battery Guide
Peripherals
Peripheral kits include isolator switches, battery cables and wiring. All of these items are essential to installing a load shedding kit correctly and safely.
Learn More
If you’d like to learn more about solar inverters and batteries, watch these videos:
Chapter 5
Load Shedding Inverter Battery Kit Prices
What to expect
Inverter Battery Equipment Costs

Kits start at around R30,000 and go up to around R80,000.
The price is determined by the brand of the equipment you want and how many batteries you require.
The better the quality, the higher the price.
Load Shedding Inverter Battery Installation Costs

You can expect the installation to cost you around R11,000.
This cost excludes pre-existing electrical issues. But it includes splitting your distribution board, installation of the equipment and wiring.
You will also get a CoC (Certificate of Compliance), which is required by law on the completion of the installation.
Chapter 6
How to Choose the Right Equipment
From start to finish
In this section, we’ll go through strategies for goals that you may have for the future and which kits would best suit these goals.
I want battery backup power, no solar
Goal:
If your goal is to only have a backup power system for when the grid is down and you have no intention of producing solar power at a later stage.
Strategy:
An Off-Grid pure sine wave inverter, preferably with a UPS is the way to go.
Alternative:
You can also have a Hybrid Inverter but in the interest of saving money, the Off-Grid Inverter will work just as well for you as you do not need the blending capabilities of a Hybrid Inverter.
Pros:
- Off-Grid Inverters are the most affordable inverters.
- Installation costs are less than that of the Solar Power Kits.
- The battery bank is expandable.
Cons:
- Can be quite noisy so bear that in mind if you are installing this system inside your home.
I want a Load Shedding backup system now and add solar later
Goal:
To slowly transform your Battery Inverter Kit into a solar power kit in the future.
Strategy:
A Hybrid is a perfect inverter for you. Hybrid Inverters blend power from all sources which means that you will be using all your produced solar power, even if you aren’t producing enough solar energy to power your essential appliances.
Alternative:
A high voltage Off-Grid Inverter, again, preferably with a UPS will work but, it’s important to remember that they do not blend power sources. If you are not producing enough solar power to supply your demand, the system will switch over to grid supply and you will lose out on that solar energy produced.
Pros:
- The blending capabilities of the Hybrid Inverter are beneficial to helping you save money.
- They are quieter than off-grid inverters and can be installed outside undercover.
- Slowly building your system is financially appealing.
- The battery bank is expandable.
Cons:
- You will need to pay an additional installation fee for the installation of the solar panels.
- Hybrid Inverters are more expensive than Off-Grid Inverters.
Chapter 7
Sizing a Battery Bank for Load Shedding
The how to
Most of us want to run our TVs, lights, modem, fridge, charge a couple of laptops and mobile phones during load shedding.
The best way to go about this is to find the power ratings of the appliances you want to run during load shedding and add their ratings up.
Example Appliances
- 2 x 120W TV – 240W
- 10 x 10W Lights – 100W
- 1 x 10W Modem – 10W
- 1 x 250W Fridge freezer – 250W
- 2 x 40W Laptop chargers – 80W
- 3 x 20W Phone chargers – 60W
Total: 740W
The Answer
Now you’ll take your 740W and times that by the two and a half hours of load shedding:
740W x 2.5hours = 1850Wh or 1.85kWh.
You’ll need a pretty small battery like a 2.4kWh battery for the chosen appliances.
TIP
Be mindful of what appliances you are running during load shedding. You may be able to get away with making a cup of tea but depending on the size of your battery and what you are running, you may deplete your battery too quickly.
Rather, make your tea before or after load shedding to avoid draining your battery too quickly.
Chapter 8
Battery Mounting
Floor, wall or rack-mounted
Wall-Mounted
If the installation site has minimal space, I highly recommend getting a wall-mounted battery. It keeps the floor clear and saves space, and makes for a neat installation.
You’ll need to be mindful of available wall space for the potential future expansion of your battery backup as wall-mounted batteries are large.
Rack-Mounted
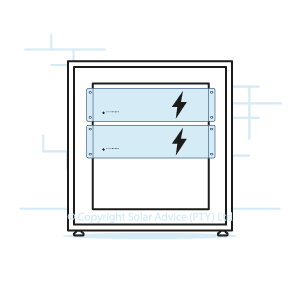
Rack-mounted batteries can be bought in smaller sized battery modules which all fit neatly into a cabinet. And adding more batteries is quick and easy.
However, these cabinets will need to have floor space. They cannot be moved around as they are incredibly heavy if they have batteries inside them.
Floor-Mounted
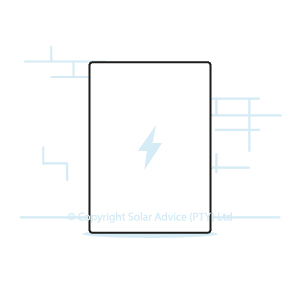
Floor-mounted batteries look very similar to wall-mounted batteries. The internal components are housed in a neat looking box.
The batteries are mounted on the floor, similar to the rack-mounted batteries but a cabinet is not required. Additionally, they are not as deep as the cabinets for the rack-mounted batteries so they take up less floor space.
Chapter 9
Load Shedding Inverter Battery Kits vs Solar Power Kits
To panel or not to panel
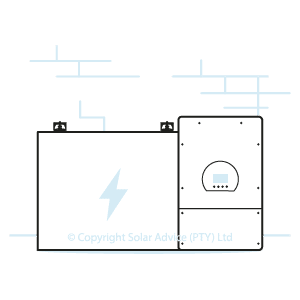
Load Shedding Inverter Battery Kit Includes
- Inverter
- Battery
- Peripherals
Solar Panels
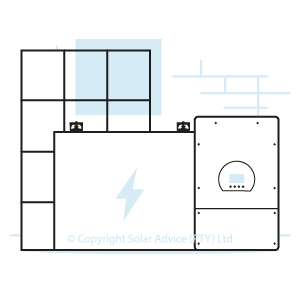
Solar Power Kit Includes
- Inverter
- Battery
- Peripherals
- Solar Panels
A great piece of information to note is that if your budget restricts you from installing a Solar Power Kit, you can install a Load Shedding Kit and add solar panels at a later stage.
Many of our clients have done this as it keeps their power on during grid failure, and in a year or two, they decide to add solar panels. It’s 100% doable and a great way to start small and grow as you need to.
To learn more about Solar Power Kits, read our: Solar Power Kits Guide
